NationalPublicData.com Hack Exposes a Nation’s Data – Krebs on Security
A great many readers this month reported receiving alerts that their Social Security Number, name, address and other personal information were exposed in a breach at a little-known but aptly-named consumer data broker called NationalPublicData.com. This post examines what we know about a breach that has exposed hundreds of millions of consumer records. We’ll also take a closer look at the data broker that got hacked — a background check company founded by an actor and retired sheriff’s deputy from Florida.
On July 21, 2024, denizens of the cybercrime community Breachforums released more than 4 terabytes of data they claimed was stolen from nationalpublicdata.com, a Florida-based company that collects data on consumers and processes background checks.
The breach tracking service HaveIBeenPwned.com and the cybercrime-focused Twitter account vx-underground both concluded the leak is the same information first put up for sale in April 2024 by a prolific cybercriminal who goes by the name “USDoD.”
On April 7, USDoD posted a sales thread on Breachforums for four terabytes of data — 2.9 billion rows of records — they claimed was taken from nationalpublicdata.com. The snippets of stolen data that USDoD offered as teasers showed rows of names, addresses, phone numbers, and Social Security Numbers (SSNs). Their asking price? $3.5 million.
Many media outlets mistakenly reported that the National Public data breach affects 2.9 billion people (that figure actually refers to the number of rows in the leaked data sets). HaveIBeenOwned.com’s Troy Hunt analyzed the leaked data and found it is a somewhat disparate collection of consumer and business records, including the real names, addresses, phone numbers and SSNs of millions of Americans (both living and deceased), and 70 million rows from a database of U.S. criminal records.
Hunt said he found 137 million unique email addresses in the leaked data, but stressed that there were no email addresses in the files containing SSN records.
“If you find yourself in this data breach via HaveIBeenPwned.com, there’s no evidence your SSN was leaked, and if you’re in the same boat as me, the data next to your record may not even be correct.”
Nationalpublicdata.com publicly acknowledged a breach in a statement on Aug. 12, saying “there appears to have been a data security incident that may have involved some of your personal information. The incident appears to have involved a third-party bad actor that was trying to hack into data in late December 2023, with potential leaks of certain data in April 2024 and summer 2024.”
The company said the information “suspected of being breached” contained name, email address, phone number, social security number, and mailing address(es).
“We cooperated with law enforcement and governmental investigators and conducted a review of the potentially affected records and will try to notify you if there are further significant developments applicable to you,” the statement continues. “We have also implemented additional security measures in efforts to prevent the reoccurrence of such a breach and to protect our systems.”
Hunt’s analysis didn’t say how many unique SSNs were included in the leaked data. But according to researchers at Atlas Data Privacy Corp., there are 272 million unique SSNs in the entire records set.
Atlas found most records have a name, SSN, and home address, and that approximately 26 percent of those records included a phone number. Atlas said they verified 5,000 addresses and phone numbers, and found the records pertain to people born before Jan. 1, 2002 (with very few exceptions).
If there is a tiny silver lining to the breach it is this: Atlas discovered that many of the records related to people who are now almost certainly deceased. They found the average age of the consumer in these records is 70, and fully two million records are related to people whose date of birth would make them more than 120 years old today.
TWISTED HISTORY
Where did National Public Data get its consumer data? The company’s website doesn’t say, but it is operated by an entity in Coral Springs, Fla. called Jerico Pictures Inc. The website for Jerico Pictures is not currently responding. However, cached versions of it at archive.org show it is a film studio with offices in Los Angeles and South Florida.
The Florida Secretary of State says Jerico Pictures is owned by Salvatore (Sal) Verini Jr., a retired deputy with the Broward County Sheriff’s office. The Secretary of State also says Mr. Verini is or was a founder of several other Florida companies, including National Criminal Data LLC, Twisted History LLC, Shadowglade LLC and Trinity Entertainment Inc., among others.
Mr. Verini did not respond to multiple requests for comment. Cached copies of Mr. Verini’s vanity domain salvatoreverini.com recount his experience in acting (e.g. a role in a 1980s detective drama with Burt Reynolds) and more recently producing dramas and documentaries for several streaming channels.
Sal Verini’s profile page at imdb.com.
Pivoting on the email address used to register that vanity domain, DomainTools.com finds several other domains whose history offers a clearer picture of the types of data sources relied upon by National Public Data.
One of those domains is recordscheck.net (formerly recordscheck.info), which advertises “instant background checks, SSN traces, employees screening and more.” Another now-defunct business tied to Mr. Verini’s email — publicrecordsunlimited.com — said it obtained consumer data from a variety of sources, including: birth, marriage and death records; voting records; professional licenses; state and federal criminal records.
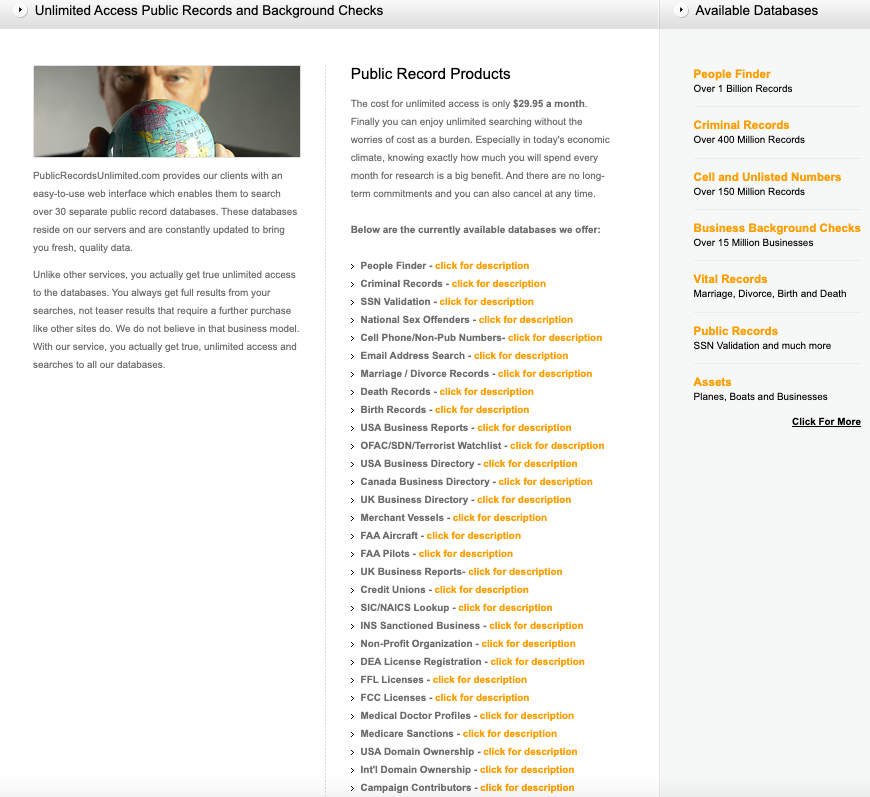
The homepage for publicrecordsunlimited.com, per archive.org circa 2017.
It remains unclear how thieves originally obtained these records from National Public Data. KrebsOnSecurity sought comment from USDoD, who is perhaps best known for hacking into Infragard, an FBI program that facilitates information sharing about cyber and physical threats with vetted people in the private sector.
USDoD said they indeed sold the same data set that was leaked on Breachforums this past month, but that the person who leaked the data did not obtain it from them. USDoD said the data stolen from National Public Data had traded hands several times since it was initially stolen in December 2023.
“The database has been floating around for a while,” USDoD said. “I was not the first one to get it.”
USDoD said the person who originally stole the data from NPD was a hacker who goes by the handle SXUL. That user appears to have deleted their Telegram account several days ago, presumably in response to intense media coverage of the breach.
ANALYSIS
Data brokers like National Public Data typically get their information by scouring federal, state and local government records. Those government files include voting registries, property filings, marriage certificates, motor vehicle records, criminal records, court documents, death records, professional licenses, bankruptcy filings, and more.
Americans may believe they have the right to opt out of having these records collected and sold to anyone. But experts say these underlying sources of information — the above-mentioned “public” records — are carved out from every single state consumer privacy law. This includes California’s privacy regime, which is often held up as the national leader in state privacy regulations.
You see, here in America, virtually anyone can become a consumer data broker. And with few exceptions, there aren’t any special requirements for brokers to show that they actually care about protecting the data they collect, store, repackage and sell so freely.
In February 2023, PeopleConnect, the owners of the background search services TruthFinder and Instant Checkmate, acknowledged a breach affecting 20 million customers who paid the data brokers to run background checks. The data exposed included email addresses, hashed passwords, first and last names, and phone numbers.
In 2019, malicious hackers stole data on more than 1.5 billion people from People Data Labs, a San Francisco data broker whose people-search services linked hundreds of millions of email addresses, LinkedIn and Facebook profiles and more than 200 million valid cell phone numbers.
These data brokers are the digital equivalent of massive oil tankers wandering the coast without GPS or an anchor, because when they get hacked, the effect is very much akin to the ecological and economic fallout from a giant oil spill.
It’s an apt analogy because the dissemination of so much personal data all at once has ripple effects for months and years to come, as this information invariably feeds into a vast underground ocean of scammers who are already equipped and staffed to commit identity theft and account takeovers at scale.
It’s also apt because much like with real-life oil spills, the cleanup costs and effort from data spills — even just vast collections of technically “public” documents like the NPD corpus — can be enormous, and most of the costs associated with that fall to consumers, directly or indirectly.
WHAT SHOULD YOU DO?
Should you worry that your SSN and other personal data might be exposed in this breach? That isn’t necessary for people who’ve been following the advice here for years, which is to freeze one’s credit file at each of the major consumer reporting bureaus. Having a freeze on your files makes it much harder for identity thieves to create new accounts in your name, and it limits who can view your credit information.
The main reason I recommend the freeze is that all of the information ID thieves need to assume your identity is now broadly available from multiple sources, thanks to the multiplicity of data breaches we’ve seen involving SSN data and other key static data points about people.
But beyond that, there are numerous cybercriminal services that offer detailed background checks on consumers, including full SSNs. These services are powered by compromised accounts at data brokers that cater to private investigators and law enforcement officials, and some are now fully automated via Telegram instant message bots. Meaning, if you’re an American who hasn’t frozen their credit files and you haven’t yet experienced some form of new account fraud, the ID thieves probably just haven’t gotten around to you yet.
All Americans are also entitled to obtain a free copy of their credit report once a year from each of the three major credit bureaus, through the website annualcreditreport.com. If you haven’t done this in a while, now would be an excellent time to order your files (or just get one now, and then a report from a different bureau in 4-5 months, and so on).
Either way, review the reports and dispute any errors you may find. Identity theft and new account fraud is not a problem that gets easier to solve by letting it fester.
Mr. Verini probably didn’t respond to requests for comment because his company is now the subject of a class-action lawsuit (NB: the lawsuit also erroneously claims 3 billion people were affected). These lawsuits are practically inevitable now after a major breach, but they also have the unfortunate tendency to let regulators and lawmakers off the hook.
Almost every time there’s a major breach of SSN data, Americans are offered credit monitoring services. Most of the time, those services come from one of the three major consumer credit bureaus, the same companies that profit by compiling and selling incredibly detailed dossiers on consumers’ financial lives. The same companies that use dark patterns to trick people into paying for “credit lock” services that achieve a similar result as a freeze but still let the bureaus sell your data to their partners.
But class-actions alone will not drive us toward a national conversation about what needs to change. Americans currently have very few rights to opt out of the personal and financial surveillance, data collection and sale that is pervasive in today’s tech-based economy.
The breach at National Public Data may not be the worst data breach ever. But it does present yet another opportunity for this country’s leaders to acknowledge that the SSN has completely failed as a measure of authentication or authorization. It was never a good idea to use as an authenticator to begin with, and it is certainly no longer suitable for this purpose.
The truth is that these data brokers will continue to proliferate and thrive (and get hacked and relieved of their data) until Congress begins to realize it’s time for some consumer privacy and data protection laws that are relevant to life in the 21st century.